Your lab results tell us the story of you.
Every biomarker we test reveals something new and unique about how your body functions. As we track these markers over time, a blueprint begins to take shape, one that helps us understand how your body adapts, where it needs support, and how to intervene with intention. This evolving insight allows us to personalize care, optimize performance, and enhance your health span.
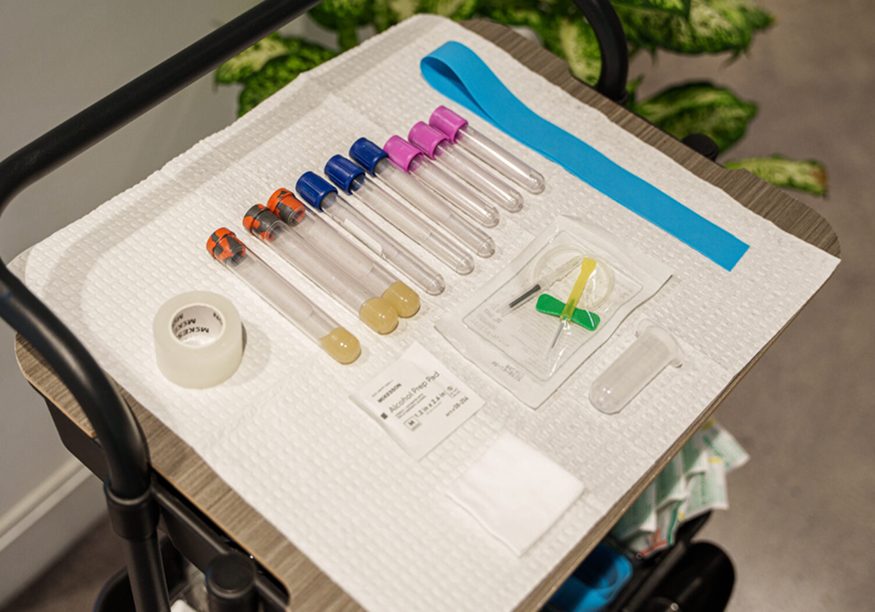
These are the biomarkers that bring clarity to your care, giving insight into the ‘why’ behind how you feel.
We’ve grouped them into key areas of your health so you can better understand what we’re testing, why it matters, and how it helps guide your care at R3 Health.

Blood
This foundational section provides insight into your oxygen delivery and overall cellular health. It sets the stage for deeper understanding and personalized care.
Tells us how many red blood cells you have. Low levels may point to anemia or low oxygen delivery in the body.
A protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout your body. It’s a key marker for energy and vitality.
Measures how much of your blood is made up of red blood cells. This helps us assess oxygen levels and hydration.
Shows the average size of your red blood cells. It helps us understand if certain nutrient deficiencies may be present.
Indicates how much hemoglobin is in each red blood cell. It gives us clues about how efficiently your blood is carrying oxygen.
Tells us how concentrated the oxygen-carrying protein (hemoglobin) is inside your red blood cells. It helps us assess how efficiently your cells are delivering oxygen.
Measures the variation in red blood cell size. A higher value may suggest nutrient deficiencies like iron, B12, or folate.
Platelets help your blood clot properly. This marker gives us insight into your body’s ability to stop bleeding and heal.
Looks at the average size of your platelets. Abnormal sizes can signal inflammation or issues with platelet production.
Identifies your blood type (A, B, AB, or O) and whether you are Rh-positive or Rh-negative. This information is important for safe blood transfusions, pregnancy care, and certain medical treatments.

Electrolytes & Fluid Balance
Electrolytes keep your muscles, nerves, and hydration levels in check. This category helps us understand how your body manages minerals and fluids.
Helps regulate how much fluid your body holds and supports proper nerve and muscle function.
Essential for keeping your heart beating normally and your muscles working the way they should.
Works with other minerals to maintain fluid balance, hydration, and your body’s pH level.
Tells us how well your body is maintaining a healthy acid-base balance, which affects breathing, kidney function, and overall metabolism.
Kidney
Supports waste removal and fluid balance. These markers show how efficiently your body is filtering and regulating essential systems.
A waste product that your kidneys filter out. Higher levels can suggest your kidneys aren't clearing waste as well as they should.
A natural byproduct from your muscles. It's another key marker of how well your kidneys are working.
Helps us understand the root cause of kidney stress, whether it’s due to hydration, diet, or something more serious.

Liver
The body’s detox powerhouse. Liver health affects hormone metabolism, digestion, and your ability to clear toxins.
A liver enzyme that helps us detect early signs of liver stress or inflammation.
Another enzyme linked to liver health, though it’s also found in muscles. It helps us interpret whether issues are liver-related or from other tissues.
An enzyme tied to your liver, bones, and bile ducts. Changes here can point to blockages or inflammation.
A substance created when red blood cells break down. Elevated levels can indicate problems with the liver or bile flow.
A key protein made by the liver. Low levels might suggest liver dysfunction or issues with protein absorption or nutrition.
Measures the combined levels of major blood proteins, offering insight into overall liver health and nutritional status.

Thyroid
A key driver of metabolism and energy. We assess thyroid performance to uncover common, but often missed, causes of fatigue, weight gain, and mood changes.
This hormone signals your thyroid to produce more thyroid hormones. It’s often the first marker we look at to assess thyroid function.
This is the active form of thyroid hormone that directly affects your energy, metabolism, and mood.
A precursor to T3, this hormone reflects how much thyroid hormone your body is making and storing.

Metabolic
How well your body processes sugar, burns fat, and maintains stable energy. This category gives early insight into insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction.
Measures your blood sugar at the time of the test. Elevated levels may be an early sign of blood sugar imbalance or insulin resistance.
Shows how your body is responding to sugar. Too much or too little can indicate issues with metabolism or energy regulation.
Gives us a long-term view of your blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months. It helps identify risks for prediabetes or diabetes even if your day-of levels look normal.

Heart
This category focuses on understanding how well your cardiovascular system is functioning, going beyond a traditional cholesterol panel. We assess blood fats, circulation, and markers of arterial health to identify early risks and support long-term heart wellness.
The overall amount of cholesterol in your blood (A combination of LDL and HDL)
Often referred to as "bad" cholesterol. High levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
Known as "good" cholesterol. It helps remove excess cholesterol from your bloodstream.
A type of fat in your blood. High levels are linked to metabolic health issues.
Measures how many LDL particles you have. A higher number is more predictive of heart disease risk than just LDL cholesterol alone.
Smaller, dense LDL particles are considered more harmful because they’re more likely to penetrate artery walls and contribute to plaque buildup.
Average size of your LDL particles. Larger particles are considered less risky.
Measures how many HDL particles are present. More is generally better.
Very-low-density lipoproteins carry triglycerides. Elevated levels are linked to increased cardiovascular risk.
A protein involved in clearing cholesterol from the bloodstream. Higher levels are generally protective for heart health.
A protein found in LDL (“bad”) cholesterol particles. Elevated levels are linked to a higher risk of plaque buildup and cardiovascular disease.

Nutrients
Even small deficiencies can make a big impact. We evaluate your nutrient stores that support biochemical processes necessary for immunity, cognition, metabolism, and performance.
Supports energy, brain health, and the production of healthy red blood cells. Low levels can lead to fatigue, brain fog, or tingling in the hands and feet.
Important for cell repair, DNA production, and red blood cell formation. Especially critical during times of growth or healing.
A powerhouse mineral involved in hundreds of body processes, including muscle function, relaxation, and steady energy levels.
Tells us how much iron is circulating in your blood. It’s essential for oxygen transport, focus, and endurance.
Reflects how much iron your body has stored. Low levels may suggest deficiency, while high levels could point to inflammation or overload.

Stress & Aging
Helps us understand how your body is responding to daily stress and the aging process. These markers guide interventions for resilience and longevity.
Often called the “stress hormone,” cortisol helps regulate your energy, blood sugar, and inflammation. Abnormal levels can indicate burnout, chronic stress, or adrenal dysfunction.
A marker related to growth hormone activity. It plays a role in cell repair, recovery, and healthy aging.
A hormone involved in stress response, hormone balance, and brain function. Levels naturally decline with age, but low levels may also reflect chronic stress or fatigue.
Female Health
Explores hormone rhythms, fertility, and mood regulation. These insights are key to supporting women through all life stages, from menstruation to menopause.
Regulates your menstrual cycle and supports ovarian function. Often tested to assess fertility and hormone balance.
Works with FSH to trigger ovulation and support the production of progesterone. Imbalances may impact cycle regularity or fertility.
The main form of estrogen in women, essential for regulating the menstrual cycle, supporting bone density, skin health, and emotional well-being.
Offers a broader view of overall estrogen levels in the body and can help assess hormonal shifts throughout different life stages.
A key hormone that balances estrogen, supports a healthy menstrual cycle, and is critical for pregnancy. Low levels may contribute to PMS, irregular cycles, or mood changes.
Influences menstrual regularity, libido, and fertility.
A protein that controls how much estrogen and testosterone are available for your body to use. Imbalances can affect hormone symptoms.
While present in smaller amounts in women, testosterone plays an important role in energy, mood, muscle tone, and libido

Male Health
Focuses on vitality, libido, and hormonal balance. These markers help us assess how lifestyle, aging, and stress are impacting male performance and wellbeing.
Supports sperm production and overall reproductive health. Low levels may affect fertility.
Signals the testes to produce testosterone. Low levels can indicate hormonal imbalance.
A form of estrogen that’s important for bone density, mood stability, and cardiovascular health in men. Elevated levels can contribute to fatigue, weight gain, or estrogen dominance symptoms.
Provides a broader view of overall estrogen levels, which impact metabolism, libido, and body composition.
A protein that binds to sex hormones like testosterone, regulating how much is available for your body to use.
Total testosterone shows overall hormone levels, while free testosterone reveals how much is active and available. Both are essential for strength, motivation, and sexual health.
A potent form of testosterone involved in muscle growth, libido, and hair development. Imbalances may contribute to hair loss or prostate concerns.
A protein made by the prostate gland. While low levels are normal, higher levels may indicate inflammation, enlargement, or in some cases, risk for prostate cancer. This test helps monitor prostate health over time.

Autoimmunity
Screens for early signs of autoimmune activity, which is when the immune system starts attacking the body’s own tissues. This is often traceable before symptoms fully develop.
Helps detect early signs of autoimmune activity. A positive result may indicate that the immune system is mistakenly attacking healthy tissues.
Commonly used to screen for autoimmune conditions that affect the joints and connective tissue, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Indicates whether the immune system is targeting the thyroid. Elevated levels are often seen in conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.

Immune Regulation
Looks at how well your immune system is functioning overall. It helps us identify imbalances that may increase susceptibility to illness or chronic conditions.
Measures the total number of white blood cells in your blood. High or low levels can indicate infection, inflammation, or immune system changes.
These are your body's first responders to bacterial infections. They help fight off illness quickly.
Key players in defending against viruses and helping regulate your immune system.
Help clean up debris from infections and are involved in longer-term immune responses.
Often elevated in people with allergies or in response to certain parasites.
Play a role in allergic reactions and inflammation by releasing histamine.

Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many modern illnesses. We evaluate your body’s baseline inflammatory state so we can reduce internal stress and promote healing.
A sensitive marker that shows low levels of inflammation in the body. Even slight elevations can signal increased risk for chronic conditions like heart disease or autoimmune issues.
An amino acid that, when elevated, can contribute to inflammation and damage blood vessels. It’s also linked to heart health, brain function, and methylation pathways.

Cancer Detection
Select markers help identify early changes that may signal a need for further evaluation. Used as part of a broader prevention strategy.
A marker sometimes used to monitor breast cancer. It may be elevated in active disease but is not used for early screening.
A general tumor marker that may be elevated in several cancers, especially of the colon and rectum.
Most commonly associated with pancreatic and gastrointestinal cancers.

Heavy Metals
Assesses toxic load from environmental exposures. High levels of metals like mercury can interfere with brain function, hormones, and detox capacity.
A toxic heavy metal that can build up in the body from environmental exposure. Even low levels can affect brain function, mood, and long-term health, especially in children and adults with chronic exposure.
An essential mineral that supports immune health, wound healing, hormone balance, and brain function. Both low and high levels can create imbalance.
Another essential mineral that works with zinc to support energy production and the nervous system. Imbalances can affect mood, immunity, and metabolism.
A toxic metal most often absorbed through certain seafood or environmental sources. High levels can impact cognitive function, immunity, and detoxification.

Sexual Wellness
We include screening for common sexually transmitted infections as part of a proactive, confidential approach to your overall health. These tests support prevention, fertility awareness, and peace of mind.
Screens for two of the most common bacterial STIs: gonorrhea (GC) and chlamydia. These infections may have no symptoms but can affect reproductive health if untreated.
A modern, highly sensitive test that detects both HIV antibodies and antigens, allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
Screens for exposure to hepatitis C, a viral infection that affects the liver.
Helps detect recent or active infection with hepatitis B, which is also spread through blood and bodily fluids.
Detects antibodies for HSV-1, typically associated with oral herpes but can also be transmitted genitally.
Detects antibodies for HSV-2, the strain most commonly linked to genital herpes. Many people carry the virus without knowing it.

